Jupiter's mass is a fascinating topic for astronomers and space enthusiasts alike. As the largest planet in our solar system, Jupiter holds a significant place in understanding planetary formation and the dynamics of celestial bodies. In this article, we will explore the extraordinary mass of Jupiter and its implications for the solar system.
Jupiter's mass is not only a scientific marvel but also a critical factor in maintaining the stability of the solar system. Its gravitational influence affects the orbits of other planets and even smaller objects like asteroids. Understanding Jupiter's mass helps scientists study the origins of the solar system and predict future celestial events.
Whether you are a student of astronomy or simply curious about space, this article will provide valuable insights into Jupiter's mass, its significance, and its role in the universe. Let's dive into the details and uncover the mysteries of this gas giant.
Read also:Unlock The Power Of Streaming Your Ultimate Guide To Vegamovies Hub
Table of Contents
- Overview of Jupiter's Mass
- Comparison with Other Planets
- Gravitational Effects of Jupiter's Mass
- Formation and History of Jupiter
- Scientific Studies on Jupiter's Mass
- Jupiter's Atmosphere and Composition
- Jupiter's Moons and Their Role
- Impact on Asteroid Belts
- Future Studies on Jupiter's Mass
- Conclusion
Overview of Jupiter's Mass
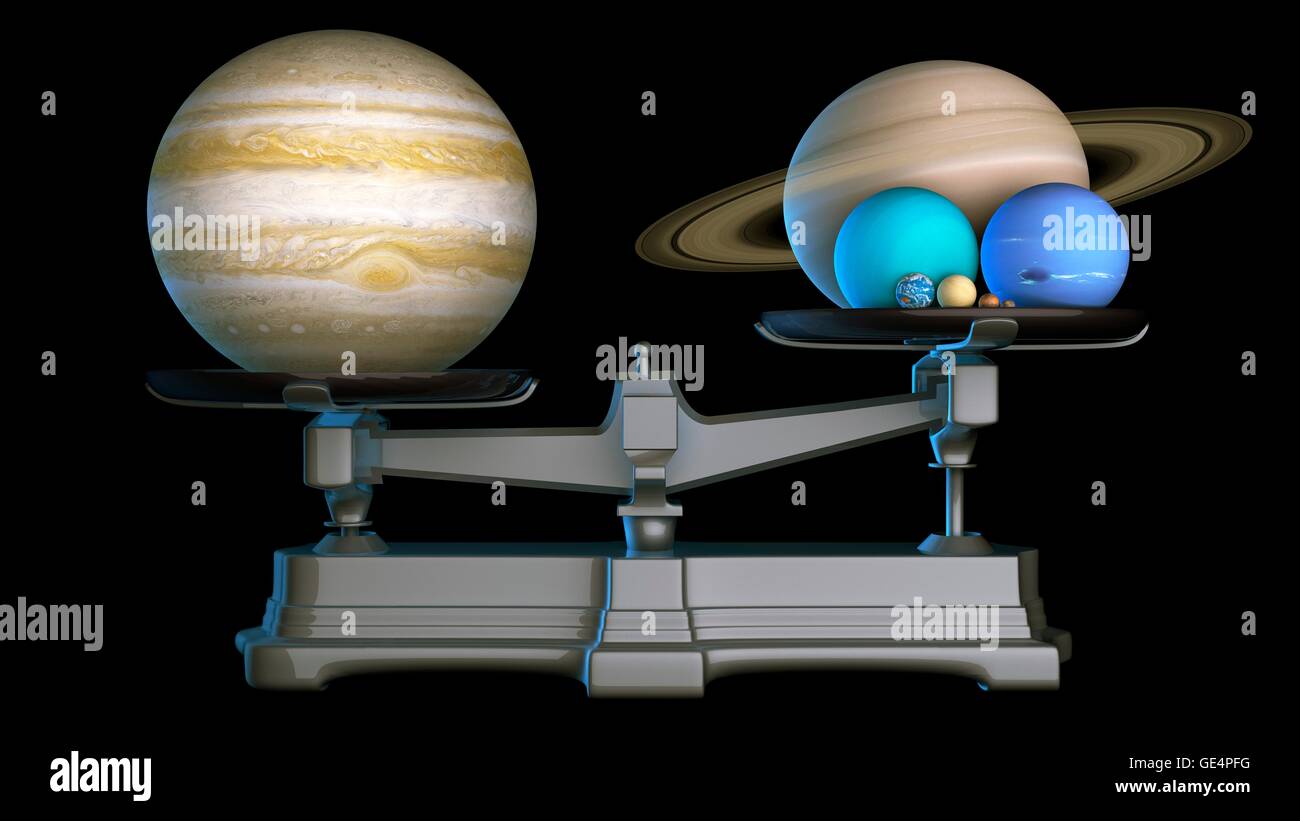
Jupiter's mass is an astonishing 1.898 × 1027 kilograms, making it the most massive planet in the solar system. This mass is approximately 318 times that of Earth, highlighting its dominance among the planets. The sheer size and mass of Jupiter play a crucial role in shaping the dynamics of the solar system.
Scientists have long been fascinated by Jupiter's mass and its implications. It not only affects the planet's own structure but also influences the orbits of neighboring celestial bodies. By studying Jupiter's mass, researchers can gain insights into the formation and evolution of the solar system.
Furthermore, Jupiter's mass is a key factor in its gravitational pull, which is the strongest among all planets. This gravitational force has significant effects on the motion of asteroids, comets, and even other planets.
Comparison with Other Planets
Size and Mass Comparison
When compared to other planets in the solar system, Jupiter's mass is unmatched. Below is a comparison of Jupiter's mass with the other planets:
- Earth: Jupiter's mass is about 318 times that of Earth.
- Saturn: Jupiter is approximately 3.3 times more massive than Saturn.
- Neptune: Jupiter's mass is roughly 19 times that of Neptune.
- Venus: Jupiter is about 270 times more massive than Venus.
This significant difference in mass highlights Jupiter's dominance in the solar system. Its immense size and mass make it a critical component in the overall structure and stability of the solar system.
Gravitational Effects of Jupiter's Mass
Impact on Nearby Objects
Jupiter's gravitational influence extends far beyond its immediate vicinity. The planet's massive size and mass create a gravitational pull that affects the orbits of nearby objects, including asteroids, comets, and even smaller moons.
Read also:Tamil Movies Online Your Ultimate Guide To Accessing Tamilblasters New Link 2025
For example, Jupiter's gravity is responsible for the existence of the asteroid belt. The planet's gravitational force prevents the asteroids from coalescing into a single body, keeping them scattered in their current orbits. Additionally, Jupiter's gravity has been known to alter the trajectories of comets, sometimes sending them on collision courses with other planets, including Earth.
Formation and History of Jupiter
Jupiter's formation dates back to the early days of the solar system, approximately 4.5 billion years ago. Scientists believe that Jupiter formed from the same cloud of gas and dust that gave birth to the Sun and other planets.
The immense gravitational pull of Jupiter allowed it to attract large amounts of hydrogen and helium, the primary components of its atmosphere. Over time, this accumulation of gas contributed to its massive size and mass. Studying Jupiter's formation provides valuable insights into the processes that shaped the solar system.
Scientific Studies on Jupiter's Mass
Research and Observations
Scientific studies on Jupiter's mass have been ongoing for decades. Researchers use advanced telescopes and space missions to gather data and refine their understanding of the planet's properties. One of the most notable missions is NASA's Juno spacecraft, which has provided valuable insights into Jupiter's atmosphere and internal structure.
Data from these studies reveal that Jupiter's mass is concentrated in its core, surrounded by layers of hydrogen and helium. The planet's rapid rotation also contributes to its oblate shape, making it slightly flattened at the poles and bulging at the equator.
Jupiter's Atmosphere and Composition
Jupiter's atmosphere is composed primarily of hydrogen and helium, with trace amounts of other elements such as methane, ammonia, and water. The planet's immense mass creates a powerful gravitational pull that traps these gases, forming a thick and dynamic atmosphere.
Scientists have observed complex weather patterns on Jupiter, including the famous Great Red Spot, a massive storm that has been raging for centuries. The planet's atmosphere is constantly in motion, driven by its rapid rotation and internal heat.
Jupiter's Moons and Their Role
Overview of Jupiter's Moons
Jupiter has a vast system of moons, with over 90 confirmed and provisional moons. Some of the most notable moons include Ganymede, Callisto, Io, and Europa. These moons play a significant role in the dynamics of the Jupiter system and are of great interest to scientists.
For example, Ganymede is the largest moon in the solar system and has its own magnetic field. Europa, on the other hand, is believed to have a subsurface ocean that may harbor conditions suitable for life. The gravitational interactions between Jupiter and its moons provide valuable insights into the planet's mass and its effects on the surrounding environment.
Impact on Asteroid Belts
Jupiter's mass has a profound impact on the asteroid belt located between Mars and Jupiter. The planet's gravitational pull prevents the asteroids from coalescing into a single body, maintaining the belt's current structure. This gravitational influence also affects the orbits of individual asteroids, sometimes sending them on collision courses with other planets.
Scientists believe that Jupiter's gravitational effects have played a crucial role in shaping the asteroid belt over billions of years. By studying the interactions between Jupiter and the asteroids, researchers can gain a better understanding of the solar system's history and evolution.
Future Studies on Jupiter's Mass
Future studies on Jupiter's mass will focus on refining current models and gathering new data through advanced space missions. Upcoming missions, such as the Europa Clipper, aim to explore the planet's moons and their potential for hosting life. These missions will provide valuable insights into Jupiter's mass, its gravitational effects, and its role in the solar system.
Additionally, scientists will continue to study Jupiter's atmosphere and internal structure using advanced telescopes and space-based observatories. These studies will help unravel the mysteries of this gas giant and its significance in the universe.
Conclusion
Jupiter's mass is a remarkable feature of this gas giant, making it the most massive planet in the solar system. Its immense size and gravitational influence shape the dynamics of the solar system and provide valuable insights into its formation and evolution. By studying Jupiter's mass, scientists can better understand the processes that govern the universe and predict future celestial events.
We invite you to share your thoughts and questions in the comments section below. If you enjoyed this article, please consider sharing it with others who might find it interesting. For more fascinating articles on astronomy and space exploration, explore our website and discover the wonders of the universe.