New York State income tax is a crucial component of the financial landscape for residents of the Empire State. Whether you're a resident, a business owner, or simply someone seeking clarity on tax obligations, understanding how New York State income tax works is essential for financial planning and compliance.
New York State income tax impacts individuals, businesses, and corporations alike. It plays a vital role in funding public services, infrastructure, and programs that benefit the community. As tax laws evolve, staying informed is key to avoiding penalties and optimizing your tax strategy.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of New York State income tax. From understanding the basics to exploring advanced concepts, our aim is to equip you with the knowledge needed to navigate this complex area of finance effectively.
Read also:Movierulz Kannada Movie Your Ultimate Guide To Kannada Film Downloads
Table of Contents
- Introduction to New York State Income Tax
- Understanding New York State Income Tax Rates
- Filing Status and Its Impact
- Deductions and Credits Available
- Important Tax Deadlines
- Tax Obligations for Non-Residents
- Business Tax in New York State
- Penalties for Late Filing or Payment
- Useful Resources for Tax Filers
- Conclusion and Next Steps
Introduction to New York State Income Tax
What is New York State Income Tax?
New York State income tax is a tax levied on the income earned by individuals, businesses, and corporations within the state. The revenue generated from this tax supports various state-funded initiatives, including education, healthcare, transportation, and public safety.
The tax system in New York operates on a progressive scale, meaning that higher income levels are taxed at higher rates. This ensures that taxpayers contribute according to their ability to pay, promoting fairness in the tax system.
For residents, understanding the nuances of New York State income tax is vital for compliance and financial planning. It involves knowing the tax rates, deductions, credits, and deadlines to avoid penalties.
Understanding New York State Income Tax Rates
Tax Brackets and Rates
New York State income tax rates are structured into several brackets based on income levels. As of the latest updates, the tax brackets for individuals are as follows:
- Income up to $8,500: 4% tax rate
- Income between $8,501 and $11,700: 4.5% tax rate
- Income between $11,701 and $13,900: 5.25% tax rate
- Income between $13,901 and $21,400: 5.97% tax rate
- Income above $21,400: Rates increase progressively up to 8.82% for the highest earners
These rates apply to residents and are subject to change based on legislative updates. It's important to stay informed about any changes to ensure accurate filing.
Filing Status and Its Impact
How Filing Status Affects Tax Liability
Your filing status determines the tax brackets and deductions you qualify for. Common filing statuses in New York include:
Read also:Jimena Herrera A Rising Star In The Entertainment Industry
- Single
- Married Filing Jointly
- Married Filing Separately
- Head of Household
Choosing the correct filing status can significantly impact your tax liability. For instance, married couples filing jointly may benefit from higher income thresholds and increased deductions compared to filing separately.
Deductions and Credits Available
Maximizing Your Tax Savings
New York State offers various deductions and credits to help taxpayers reduce their taxable income. Some of the most common include:
- Personal Exemption: A deduction for each taxpayer and dependent.
- Child Tax Credit: A credit for qualifying children under a certain age.
- Education Credits: Credits for tuition and related expenses.
- Homeowners' Property Tax Credit: A credit for homeowners paying property taxes.
Understanding these deductions and credits can help you optimize your tax strategy and minimize your tax burden.
Important Tax Deadlines
Stay on Top of Your Tax Obligations
Knowing the tax deadlines is crucial to avoid penalties. The standard deadline for filing New York State income tax returns is April 15th each year. However, if this date falls on a weekend or holiday, the deadline may be extended to the next business day.
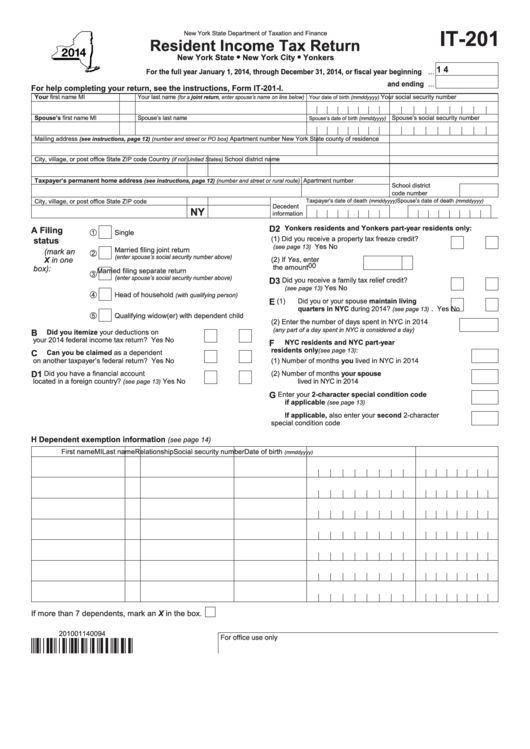
If you're unable to meet the deadline, you can request an extension by filing Form IT-201. Keep in mind that an extension only grants additional time to file; any taxes owed must still be paid by the original deadline to avoid interest and penalties.
Tax Obligations for Non-Residents
Understanding Non-Resident Tax Rules
Non-residents who earn income in New York State are also required to file state income tax returns. This includes individuals who work remotely for a New York-based employer or own property within the state.
The tax rates for non-residents are generally the same as for residents, but the calculation may differ based on the source of income. Non-residents must file Form IT-203 to report their New York-sourced income.
Business Tax in New York State
Tax Obligations for Businesses
Businesses operating in New York State are subject to various taxes, including corporate income tax, sales tax, and payroll tax. The corporate income tax rate is currently 6.5% for most corporations, with additional surcharges for businesses with higher taxable income.
Small businesses may qualify for certain exemptions or credits, such as the Small Business Credit or the Qualified Emerging Technology Company Credit. It's essential for business owners to consult with a tax professional to ensure compliance and take advantage of available incentives.
Penalties for Late Filing or Payment
Avoiding Penalties and Interest
Failing to file or pay your New York State income tax on time can result in significant penalties and interest charges. The penalty for late filing is 5% of the unpaid tax for each month or part of a month the return is late, up to a maximum of 25%.
Similarly, late payment penalties are assessed at 0.5% per month on the unpaid tax, with a cap of 25%. Interest is also charged on unpaid taxes at the federal short-term rate plus 2%.
To avoid these penalties, it's crucial to file and pay your taxes on time. If you're unable to meet the deadline, consider filing for an extension or setting up an installment agreement with the New York State Department of Taxation and Finance.
Useful Resources for Tax Filers
Where to Find More Information
Several resources are available to assist taxpayers in understanding and filing their New York State income tax returns:
- New York State Department of Taxation and Finance: The official website provides comprehensive information on tax laws, forms, and filing procedures.
- IRS Website: For federal tax guidance and updates that may impact state tax obligations.
- Tax Professionals: Certified Public Accountants (CPAs) and Enrolled Agents (EAs) can provide personalized advice and assistance.
Utilizing these resources ensures that you have access to the latest information and expert guidance when navigating the complexities of New York State income tax.
Conclusion and Next Steps
New York State income tax is a critical aspect of financial management for residents, businesses, and non-residents alike. By understanding the tax rates, filing statuses, deductions, and deadlines, you can ensure compliance and optimize your tax strategy.
We encourage you to take action by reviewing your tax situation, consulting with a professional if needed, and utilizing the available resources to stay informed. Your feedback and questions are valuable, so please leave a comment or share this article with others who may benefit from it. For more insights on financial planning and tax strategies, explore our other articles and guides.